网络版的 极简日志交互
你的环境:
- 系统 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- 直接使用其终端
- Python 2.7.10
要求:
- 每次运行时合理的打印出过往的所有笔记
- 一次接收输入一行笔记
- 在服务端保存为文件:
- 在所有访问的客户端可以获得历史笔记
- 支持多个客户端同时进行笔记记录
- 在所有访问的客户端可以获得历史笔记
1 原型
- 网络开发 明确如何进行
- UDP协议
- 简单的UDP服务器/客户端
以上都是些什么啊? 你完全摸不着头脑
尝试 探索
- 线索1 socket python doc socket
什么是 networking interface?
In computing, a network interface is a system's (software and/or hardware) interface between two pieces of equipment or protocol layers in a computer network.
A network interface will usually have some form of network address.[1] This may consist of a node Id and a port number or may be a unique node Id in its own right.
Network interfaces provide standardized functions such as passing messages, connecting and disconnecting, etc.
网络接口
- 计算机网络中 设备or协议层之间的接口
- 有网络地址:节点id or port nubmer(类似电话号码么?)
- 提供标准函数:传输信息 连接 断连
-
- 通讯endpoint
- 通讯 based on IP internet protocol
A network socket is an endpoint of an inter-process communication across a computer network. Today, most communication between computers is based on the Internet Protocol; therefore most network sockets are Internet sockets.
那到底是什么是 socket ?
Socket的英文原义是“孔”或“插座”。作为BSD UNIX的进程通信机制,取后一种意思。通常也称作"套接字",用于描述IP地址和端口,是一个通信链的句柄,可以用来实现不同虚拟机或不同计算机之间的通信。
在Internet上的主机一般运行了多个服务软件,同时提供几种服务。每种服务都打开一个Socket,并绑定到一个端口上,不同的端口对应于不同的服务。 Socket正如其英文原意那样,像一个多孔插座。一台主机犹如布满各种插座的房间,每个插座有一个编号,有的插座提供220伏交流电, 有的提供110伏交流电,有的则提供有线电视节目。 客户软件将插头插到不同编号的插座,就可以得到不同的服务

- 常用函数
- 创建
- 绑定
- 接收
- 发送
- 接收连接请求
就是用来 计算机之间 通信 的 然后你将本科的信息技术教程拿出来查看了 恩 你居然没有卖掉。。。
- TCP/IP协议标准
- 计算机网络中通信问题分为4层:Internet protocol suite
- 应用层 Application layer
- 传输层 Transport layer (包含UDP协议)规定怎样进行端-端的数据传输
- 网络互联层 Internet layer
- 网络接口 和 硬件层 Link layer
- 计算机网络中通信问题分为4层:Internet protocol suite
- UDP协议 User_Datagram_Protocol
- 属于传输层
使用UDP协议时 网络只是尽力而为地进行快速数据传输 不保证传输的可靠性
- 属于传输层
- Python 实践 1
例子1:Python doc Example
ex1_server.py
# coding=utf-8
# refet to https://docs.python.org/2/library/socket.html?highlight=socket#example
import socket
HOST = ''
PORT = 50007
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.bind((HOST, PORT))
s.listen(1)
conn, addr = s.accept()
print 'connected by', addr
while 1:
data = conn.recv(1024)
if not data: break
conn.sendall(data)
conn.close()
ex1_client.py
# coding=utf-8
import socket
HOST = 'daring.cwi.nl'# the remote host
PORT = 50007
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect((HOST, PORT))
s.sendall('hello, world')
data = s.recv(1024)
s.close()
print "received", repr(data)
1个 Terminal 中执行 python ex1_server.py 另一个 Terminal中执行 python ex1_client.py
按照教程中的来 居然出错了 error
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "ex1_client.py", line 8, in <module>
s.connect((HOST, PORT))
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/socket.py", line 228, in meth
return getattr(self._sock,name)(*args)
socket.error: [Errno 110] Connection timed out
链接超时 host的问题么? 尝试修改host 与port
HOST = 'localhost'# the remote host
PORT = 8001
OK 成功 执行 ex1_server.py的终端 打印
connected by (addr地址)
执行 ex1_client.py的终端 打印
received 'hello, world'
恩 server 端 要:
- 1 创建socket对象 调用socket函数
- socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
- 2 bind 绑定主机 s.bind((HOST, PORT)) Host主机 于端口PORT
- 3 listen 监听 s.listen(backlog) # baclog 至少为1 多个 就是可以监听多个客户端
- 4 服务器通过socket的accept method等待客户请求链接
- connection, address = socket.accept()
- accept() 返回tuple (connection, address)
- connection 表示socket 对象 服务器必须通过它与client通信
- address 表示客户端的Internet address
- 5 处理:
- 服务器 和 客户端 通过send 和 recv 通信
- 6 通信结束 使用 close方法 关闭 sock.close() or connection.close()
恩 client 端编写要:
- 1 创建socket对象 链接
- 2 知道主机 地址 和 主机建立链接
- sock.connect(host_address) # host_address = (HOST, PORT)
- 3 处理:
- 通信 send 和 recv
- 4 通信结束 sock.close() 关闭
实践 客户端请求打印过去日志
服务端:diary_serve.py:
# coding:utf-8
import socket
import jeremiah_diary
pastlog_keyword = "p"
# main
def main():
# creat 创建
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
host_address = ('localhost', 8001)
# bind
sock.bind(host_address)
# listen
sock.listen(3)
# interact 交互
while True:
print "\n Now Please input"
connection, address = sock.accept()
data = connection.recv(1024) # reveive message from client
print "You have received message from {0}".format(data)
if data == "p":
past_logs = jeremiah_diary.read_diary()
connection.sendto(past_logs, address) # print past logs
# write new logs
connection.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
客户端:diary_client.py:
import socket
def HELP():
""" # Dear , Here is the Help Doc:
1 Input: p/past , print past logs
"""
print HELP.__doc__
# Creat socket
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
host_address = ('localhost', 8001)
sock.connect(host_address) # 和server 建立联系
# 交互
pastlog_keyword = raw_input("Wanna read past logs? Input p --->")
sock.sendto(pastlog_keyword, host_address)
back_message = sock.recv(1024)
print "Here is the past logs:---> \n" , back_message
sock.close()
jeremiah_diary.read_diary() 为你编写的jeremiah_diary.py脚本 内置函数 read_diary()
def read_diary():
current_dir = os.getcwd() # 打印之前日志
os.chdir(current_dir)
filename_plus_content =""
for file in glob.glob("*.log"):
# print(file) # this is the file name
file_content = open(file, "r")
diary = file_content.read() + "\n"
filename_plus_content = filename_plus_content + file + "--->:" +diary
print filename_plus_content
return filename_plus_content
效果:
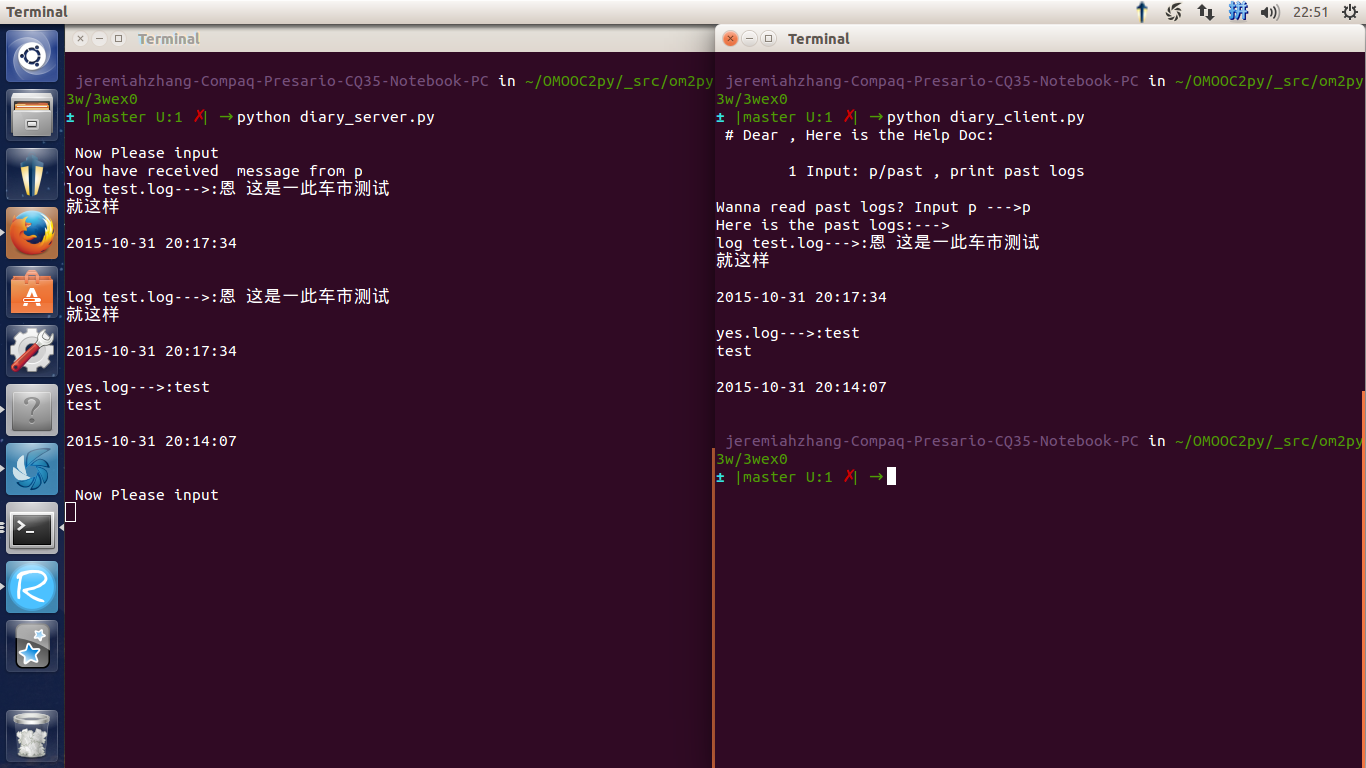
消息接收
问题
- 客户端 要
- 连续发送中文 raw_input + 循环
服务器 要
- 接受 客户端 信息 中文
- 立即保存为文件
保存到服务端
尝试 1 持续输入
diary_server.py 部分修改
while True: print "Please Wait:---> "
connection, address = sock.accept()
data = connection.recv(1024) # reveive message from client print "You have received message from {0}".format(address)
if data == "p":
past_logs = jeremiah_diary.read_diary() connection.sendto(past_logs, address) # print past logsif data == "h":
help_doc = "balabala" connection.sendto(help_doc, address)else:
diary_name = "jeremiah_diary.log" diary_writer = open(diary_name, "a+") diary_writer.write(data) back_message = "Continue to Write:--->" connection.sendto(back_message, address)connection.close()
if name == 'main': main()
diary_client.py 部分修改:
# Creat socket
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
host_address = ('localhost', 8001)
sock.connect(host_address)
# continue interact
done = False
while done==False:
pastlog_keyword = raw_input("Please write here Dear! --->")
sock.sendto(pastlog_keyword, host_address)
back_message = sock.recv(1024)
print back_message
sock.close()
出现问题:
Please write here Dear! --->this is right Continue to Write:---> Please write here Dear! --->ok Traceback (most recent call last): File "diary_client.py", line 26, in
sock.sendto(pastlog_keyword, host_address) socket.error: [Errno 32] Broken pipe
在客户端第二次输入后 终端 出现 Broken pipe 的错误
- 发现 建立socket中要使用 sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)通信SOCK_DGRAM 原来这里建立socket的时候 就设定 通信协议 以及是IPv4还是v6的, 还有是TCP/IP 和UDP
发现要使用UDP的 重新来过参考tutorial 你发现自己把TCP的和UDP的methond 混在一起了 !!! 原来以上都是在使用TCP协议的!!!
参考学习 programming-udp-sockets-in-python
需要安转 netcat ubuntu install
Install on Ubuntu $ sudo apt-get install netcat-traditional netcat-openbsd nmap To use netcat-openbsd implementation use "nc" command. To use netcat-traditional implementation use "nc.traditional" command To use nmap ncat use the "ncat" command.
learn ncat - Concatenate and redirect sockets
参考学习 programming-udp-sockets-in-python 之后
server.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import socket
import sys
import jeremiah_diary
def help():
""" # this is the help doc:
1- read past logs? enter:---> p
2- want leave ?enter:---> e
3- help doc? enter:---> h
"""
HOST = '' # Symbolic name meaning all available interfaces
PORT = 8888 # Arbitrary non-privileged port
# UDP SOCKET
try:
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
print "socket created! "
except socket.error, msg :
print "failed to created socket. ERROR code : " + str(msg[0]) + " message " + msg
sys.exit()
# bind socket to localhost and port
try:
s.bind((HOST, PORT))
except socket.error, msg:
print "bind failed. error code: " + str(msg[0]) + " message " + msg[1]
sys.exit()
print "socket bind complete"
def responses():
if data =="e":
sys.exit()
elif data =="p":
reply = jeremiah_diary.read_diary()
elif data == "h":
reply = help.__doc__
else:
diary_name = "jeremiah_diary.log" # 写日志
diary_writer = open(diary_name, "a+")
diary_writer.write(data + "\n")
diary_writer.close()
reply = "Continue to Write:--->"
return reply
# communicate with the client
while 1:
# receive from client
d = s.recvfrom(1024)
data = d[0] # client message
addr = d[1] # client address addr = (host, port)
reply=responses()
s.sendto(reply, addr)
print "message from [ " + addr[0] + ":" + str(addr[1]) + "] is --->" + data.strip()
s.close()
client.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import socket
import sys
# create dgram udp socket
try:
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
except socket.error:
print "Failed to create socket"
sys.exit()
host = "localhost"
port = 8888
print "please enter h to see the help.-->"
while 1:
msg = raw_input("Enter message to send: ---> ")
try :
# send the whole string
s.sendto(msg, (host, port)) # send to serve
# receive data from server
d = s.recvfrom(1024)
reply = d[0]
addr = d[1]
print "server reply: ---> " + reply
except socket.error, msg:
print "error code: " + str(msg[0]) + " message " + msg[1]
sys.exit()
这下 可以直接
- 打印日志
- 写日志了
执行:
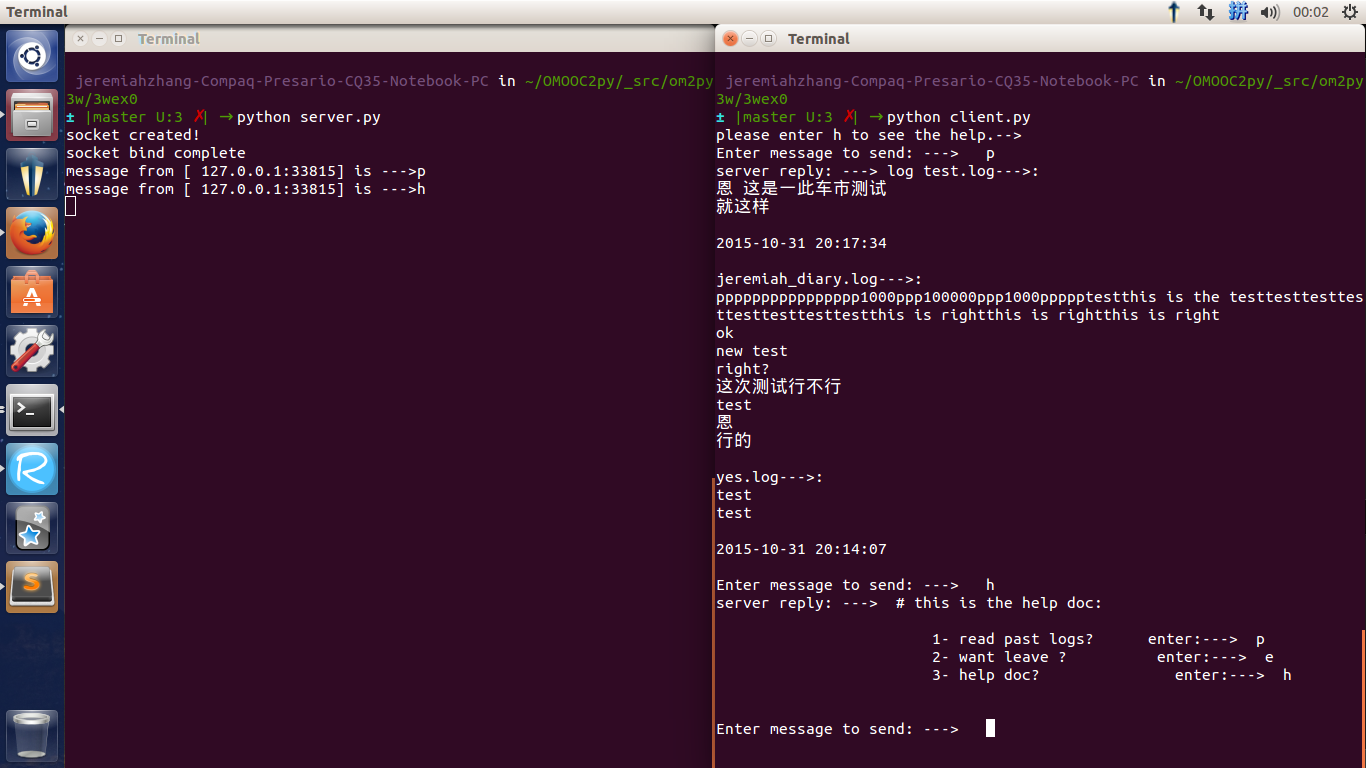
3 多个客户端
- 什么是客户端呀?
- 客户可以在客户端 向主机服务器发送消息
- 和服务器有什么关系?
- 客户端发送 服务器确认 接受信息 反馈等
- 多个客户端发送消息 给服务器 对服务器会有影响么?什么影响?
- 要排队么?
- 不知晓了
- 多个客户端可以反复获得历史消息么?
- 历史消息 已经发送给服务器了
- 如何获得历史消息?
- 客户端要向服务器请求
- 服务器再发过来 尝试 复制client.py的代码 修改 host参与 port 是不行的
学习 Tutorial on Network Programming with Python
- 尝试 在 服务器端 d = s.recvfrom(1024) 接受信息时候 启用 s.setblocking(0) 无效果
如何 多个客户端发送消息给服务器呢? 想不到办法解决呀! (上面最 近的代码只能一次处理一个客户端的请求呀)
- ptyhon 网络编程 提到类似问题 需要分叉 与 线程 需要使用 SocketServer socketserve doc 相关模块 好像又不用socket模块 如何解决呢? 之后再尝试吧 先解决 历史消息获取问题去
- 支持多个客户端同时进行笔记记录 还未实现 的继续探索
- 咦 你发现将client.py脚本 移动到另一个文件夹中 然后使用python调用 可以与服务器通信 这样
- 恩 同一个文件中的两个cilent是无法同时和server通信的 它们使用同一个port 所以无法同时通信
4 历史消息获取
客户端一启动 如何获得服务端的历史消息?
- 一启动 发送指令 请求服务器发送过来
这个好解决 只要在 client.py中添加一个 打印过去日志的指令 while 前添加
# print past logs when start s.sendto("p", (host, port)) d = s.recvfrom(1024) reply = d[0] print "Past logs: ---> \n" + reply
- 运行过程中 又反复获得 历史消息 可以吗?
- 你该如何实现呢?
- 运行过程中 反复获得历史消息
- 上面 程序 可以直接 按 p 打印过去日志了
总
- 在探索的过程中 解决问题的也就那几步
- 找到 socket UDP 基础模板 学习理解
- 类比 来解决自己问题
- 在自个儿解决中 没有从解决问题中来学习
- 先去查了资料(比较杂)居然从 socket TCP开始了 无脑思考
- 然后开始编程
- 其实应该
- 找到关键资料:如这里是 socket UDP编程 就锁定关键词
- 立即开始编程
- 在编程中 再去学习 相关内容
- 恩 整理时候 直接用github commit的link 这样 就不用在这里一次次copy自己的代码了
记住:
- 最小代价解决问题呀
- 冷静 冷静 冷静 自个儿要有自个儿的节奏
星期一, 02. 十一月 2015 09:42下午
星期三, 04. 十一月 2015 08:12下午 修改